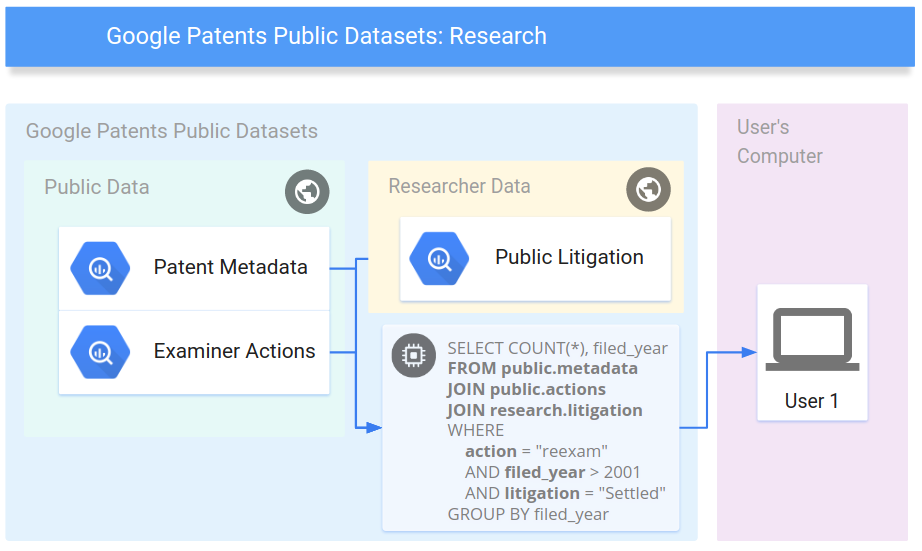
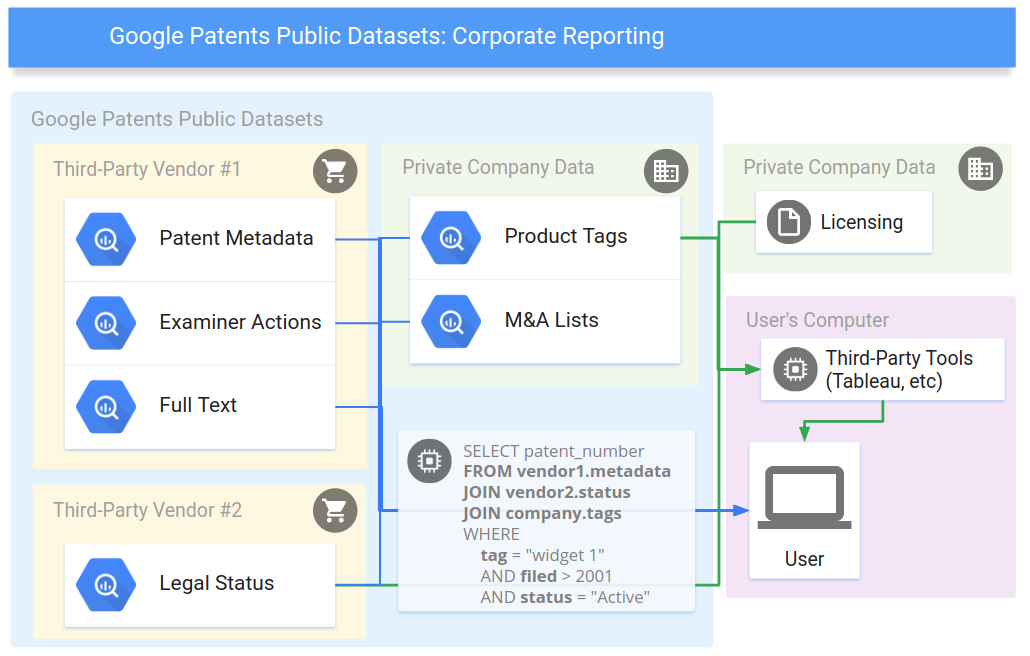
1 INTRODUCTION
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 PURPOSE
Being better at tracking the stuff you have is a great way to make more money.
When you track your products, you can predict how much you’ll sell in the future, find them faster for your customers, and reorder before you run out of product. How novel!
One of the best ways to do all that tracking, predicting, and reordering is to use an Inventory Management System.
Inventory Management System software is used for tracking inventory levels, orders, sales and deliveries. Companies can use inventory management software to avoid product overstock and outages. It is a tool for organizing inventory data that before was generally stored in hard-copy form or in spreadsheets.
1.2 WHAT IS AN INVENTORY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM?
Inventory management systems track goods through the entire supply chain or the portion of it a business operates in. That covers everything from production to retail, warehousing to shipping, and all the movements of stock and parts between.
Practically, it means a business can see all the small moving parts of its operations, allowing it to make better decisions and investments. Different inventory managers focus on different parts of the supply chain—though small businesses are usually more interested in the ordering and sales end of the chain.
1.3 ADVANTAGES OF ERP INVENTORY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
There are several advantages to using inventory management software in a business setting.
Cost savings
A company’s inventory represents one of its largest investments, along with its workforce and locations. Inventory management software helps companies cut expenses by minimizing the amount of unnecessary parts and products in storage. It also helps companies keep lost sales to a minimum by having enough stock on hand to meet demand.
Warehouse organization
As businesses move away from pen and paper processes to automated solutions, visibility becomes a key factor in inventory management.
Inventory management software can help distributors, wholesalers, manufacturers and retailers optimize their warehouses. If certain products are often sold together or are more popular than others, those products can be grouped together or placed near the delivery area to speed up the process of picking.
By 2018, 66% of warehouses “are poised to undergo a seismic shift, moving from still prevalent pen and paper processes to automated and mechanized inventory solutions. With these new automated processes, cycle counts will be performed more often and with less effort, increasing inventory visibility, and leading to more accurate fulfillment, fewer out of stock situations and fewer lost sales. More confidence in inventory accuracy will lead to a new focus on optimizing mix, expanding a selection and accelerating inventory turns.”
Updated data
Up-to-date, real-time data on inventory conditions and levels is another advantage inventory management software gives companies. Company executives can usually access the software through a mobile device, laptop or PC to check current inventory numbers. This automatic updating of inventory records allows businesses to make informed decisions.
Data security
With the aid of restricted user rights, company managers can allow many employees to assist in inventory management. They can grant employees enough information access to receive products, make orders, transfer products and do other tasks without compromising company security. This can speed up the inventory management process and save managers’ time.
Insight into trends
Tracking where products are stocked, which suppliers they come from, and the length of time they are stored is made possible with inventory management software. By analysing such data, companies can control inventory levels and maximize the use of warehouse space. Furthermore, firms are more prepared for the demands and supplies of the market, especially during special circumstances such as a peak season on a particular month. Through the reports generated by the inventory management software, firms are also able to gather important data that may be put in a model for it to be analyzed.
2 PARTS OF INVENTORY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
2.1 LOGGING ON AND LOGGING OFF

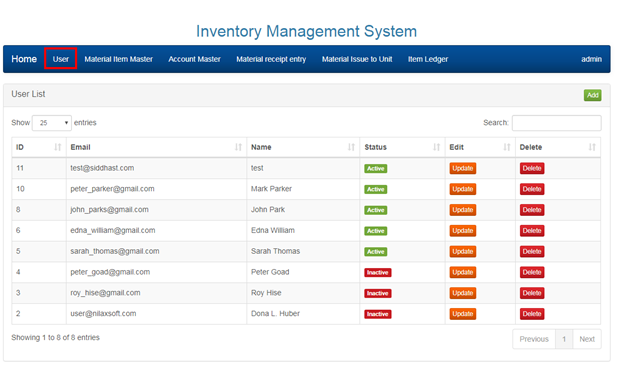
2.2 MANAGING USERS
2.3 MANAGING INVENTORY

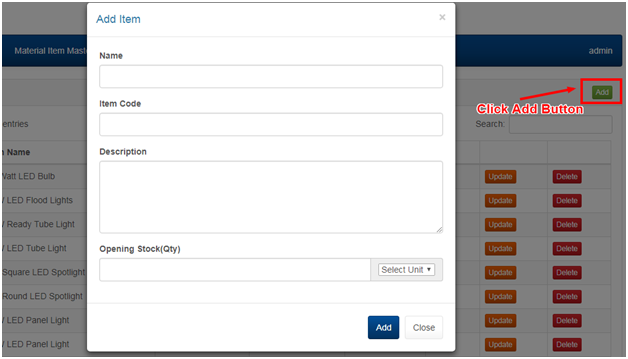
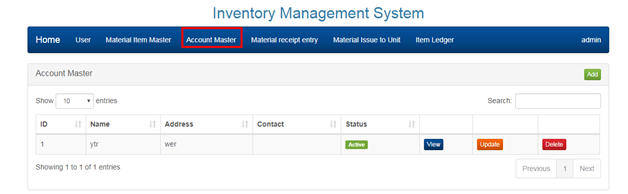
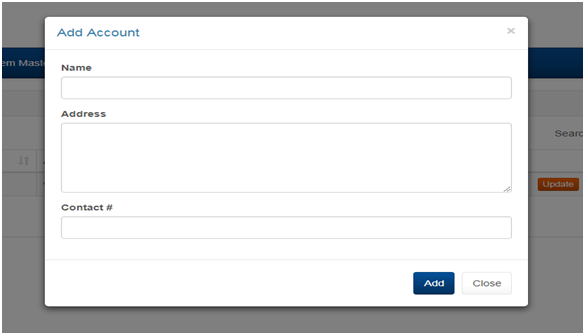
2.4 MANAGING ACCOUNTS
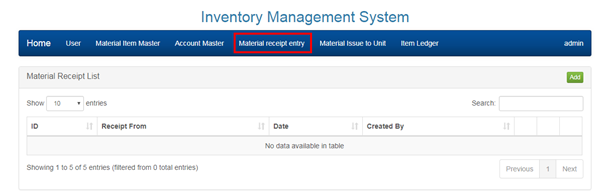
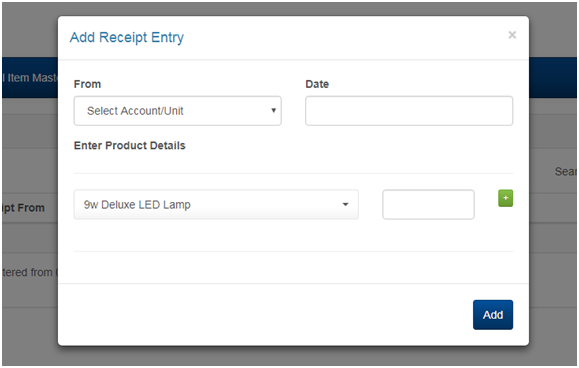
2.5 MANAGING MATERIAL RECEIPT ENTRY